Allyltributyltin, also known as allyltri-n-butylstannane, is organic compound with the CAS Number 24850-33-7. This compound has garnered significant attention in the field of organic synthesis due to its unique properties. In this blog post, SACH, as high purity active raw material exporter, will share the physical properties and applications of organic compound allyltributyltin for sale.
Properties of Organic Compound Allyltributyltin
Density
The density of allyltributyltin (CAS No.: 24850-33-7) is a crucial physical property that provides insight into its mass per unit volume. At 25 °C, the density of this compound is 1.068 g/mL. This value is particularly important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps in the accurate measurement and handling of the compound in laboratory and industrial settings. For instance, when preparing solutions or mixtures, knowing the density allows chemists to precisely calculate the amount of allyltributyltin needed based on its volume. Additionally, density plays a role in the separation and purification processes, as compounds with different densities can be separated through techniques like centrifugation or density gradient methods.
Boiling Point
The boiling point of allyltributyltin (CAS No.: 24850-33-7)is another significant physical property. It is reported to be 312.3±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg. This relatively high boiling point indicates that allyltributyltin remains in the liquid phase over a wide temperature range, which is advantageous for many organic synthesis reactions. High boiling points are often desirable in organic chemistry because they allow for reactions to be carried out at elevated temperatures without the compound vaporizing excessively. This stability at high temperatures can enhance reaction rates and improve the efficiency of certain chemical processes. Moreover, the boiling point is a key factor in distillation procedures, where precise control of temperature is necessary to separate and purify compounds based on their volatility.
Molecular Formula and Weight
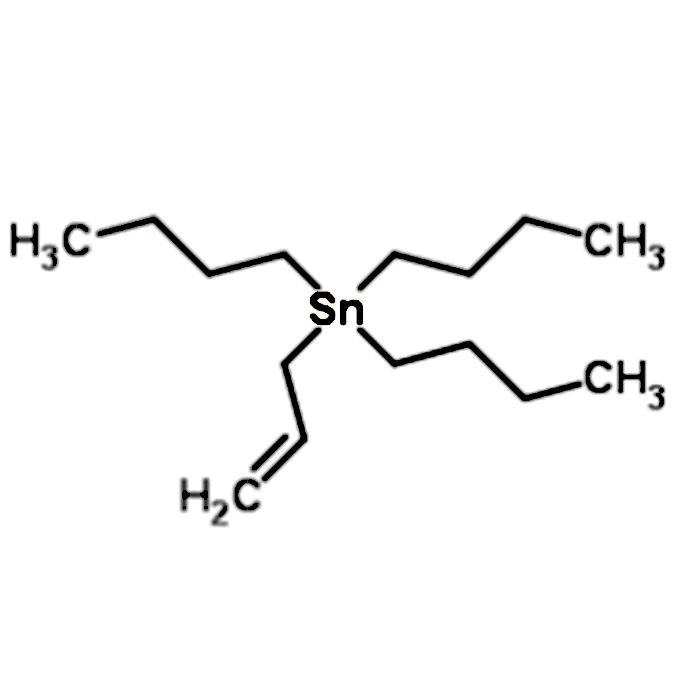
The molecular formula of allyltributyltin is C15H32Sn, and its molecular weight is 331.125 g/mol. The molecular formula provides a detailed account of the types and numbers of atoms present in the compound, which is fundamental to understanding its chemical structure and reactivity. The presence of a tin atom (Sn) in the molecule is particularly noteworthy, as tin-based compounds often exhibit unique properties and reactivities compared to their carbon-based counterparts. The molecular weight is also a critical parameter in stoichiometric calculations, which are essential for determining the amounts of reactants and products in chemical reactions. Accurate knowledge of the molecular weight ensures that chemists can precisely control the molar ratios of reactants, thereby optimizing reaction yields and minimizing waste.
Flash Point
The flash point of allyltributyltin is 146.6±13.0 °C. This property is of utmost importance in terms of safety, especially when handling and storing the compound. The flash point is the lowest temperature at which the vapor of a liquid can ignite in the presence of an ignition source. A high flash point indicates that allyltributyltin is relatively non-volatile and less likely to form flammable vapors at ambient temperatures. This reduces the risk of accidental fires and explosions, making it safer to work with in both laboratory and industrial environments. However, it is still crucial to adhere to proper safety protocols and storage conditions to ensure the compound remains stable and secure.
Appearance and Storage Conditions
Allyltributyltin (CAS No.: 24850-33-7)is described as a colorless to slightly yellowish oily liquid. Its appearance can provide valuable information about its purity and quality. A clear, colorless liquid typically indicates a high degree of purity, while any discoloration may suggest the presence of impurities or degradation products. The compound is recommended to be stored at a temperature range of 2-8℃. This specific storage condition is essential to maintain the stability and integrity of the compound. Proper storage prevents decomposition, oxidation, or other undesirable reactions that could alter the properties and effectiveness of allyltributyltin. It is also important to avoid contact with oxides, moisture, or humidity, as these can react with the compound and lead to degradation.
Stability
Allyltributyltin (CAS No.: 24850-33-7)is stable when used and stored according to specifications. It will not decompose under normal conditions, which is a significant advantage for its application in organic synthesis. Stability is a critical factor in the selection of reagents for chemical reactions, as unstable compounds can introduce unwanted side reactions or impurities. The stability of allyltributyltin ensures that it can be reliably used in a variety of reactions without the risk of spontaneous decomposition. However, it is important to note that certain conditions, such as exposure to oxides, moisture, or humidity, should be avoided to prevent any potential degradation.
Applications of Compound Allyltributyltin in Organic Synthesis
The physical properties of allyltributyltin contribute to its wide range of applications in organic synthesis. It is commonly used in addition reactions, elimination reactions, and rearrangement reactions. The stability and reactivity of the compound make it a valuable reagent for these processes. For example, in addition reactions, allyltributyltin can react with various electrophiles to form new carbon-carbon or carbon-heteroatom bonds. In elimination reactions, it can facilitate the removal of a leaving group, leading to the formation of double or triple bonds. Additionally, in rearrangement reactions, allyltributyltin can undergo structural transformations to produce more stable or desired products. The versatility of allyltributyltin in these reactions is largely due to its unique physical properties, which allow it to participate in a variety of chemical transformations under controlled conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the physical properties of allyltributyltin (CAS No.: 24850-33-7), including its density, boiling point, molecular formula and weight, flash point, appearance, storage conditions, and stability, play a pivotal role in its behavior and application in organic synthesis. These properties not only determine how the compound should be handled and stored but also influence its reactivity and effectiveness in various chemical reactions. Understanding and appreciating these physical properties are essential for chemists to utilize allyltributyltin efficiently and safely in their research and industrial processes. As a reliable and versatile reagent, allyltributyltin continues to be an important compound in the field of organic chemistry, contributing to the development of new synthetic methods and the production of valuable chemical products.
www.hzsqchem.com
SACH

